Toggle through the accordions below to download all of our project outputs, spanning our succinct Energy Reads, project information, and publications and deliverables.
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. Each one is paired with a complementary ‘infographic’ that tells the story visually.
This SONNET Toolkit of resources and guides will help you to harness the full potential of social innovation in energy transitions. Click on the cover image to flip through the toolkit in full and access our five Energy Reads, five Infographics, Power Guide, City Lab Guide, citizen survey results, SONNET videos, and Policy Brief >>
SONNET Energy Read #5: How social innovations can meet EU goals, and how EU policies can support social innovations
April 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. This Energy Read connects on-the-ground SIE-initiatives and the EU, examining how local efforts help meet EU ENergy goals, and how the EU can support SIEs in order to better harness their full, transformative potential.
SONNET Energy Read #4: Insights from six countries on the transformative contributions and effects of social innovations in energy transitions
April 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. This Energy Read defines and makes use of the concept of “institutions” to overview how social innovations can be (and are!) transformative.
SONNET Energy Read #3: Insights from the SONNET City Labs and recommendations for cities interested in experimenting with the City Lab format
March 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. This Energy Read overviews key findings from the project’s City Labs.
SONNET Energy Read #2: Key findings from Case Studies exploring how social innovations in energy shape – and are shaped by – larger systems
November 2021 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. This Energy Read overviews key findings from the project’s 18 Case Studies and three Country Reports.
SONNET Energy Read #1: About the social dimension of energy transitions
June 2020 – Download
Authors: Niklas Mischkowski (ICLEI Europe), Julia Wittmayer (DRIFT)
In this first SONNET Energy Read, we introduce the concept of social innovation in energy transitions and show their diversity, going ‘beyond only energy cooperatives’. This diversity is portrayed in a typology and illustrated with examples, putting an emphasis on the six cities that are partners in the SONNET project. Ultimately, through this Energy Read we will see that energy transitions have inseparable social and technological dimensions to them. We hope that, by understanding these dimensions, we can support the social dynamics that are necessary to the success of the much-needed renewal of our energy systems.
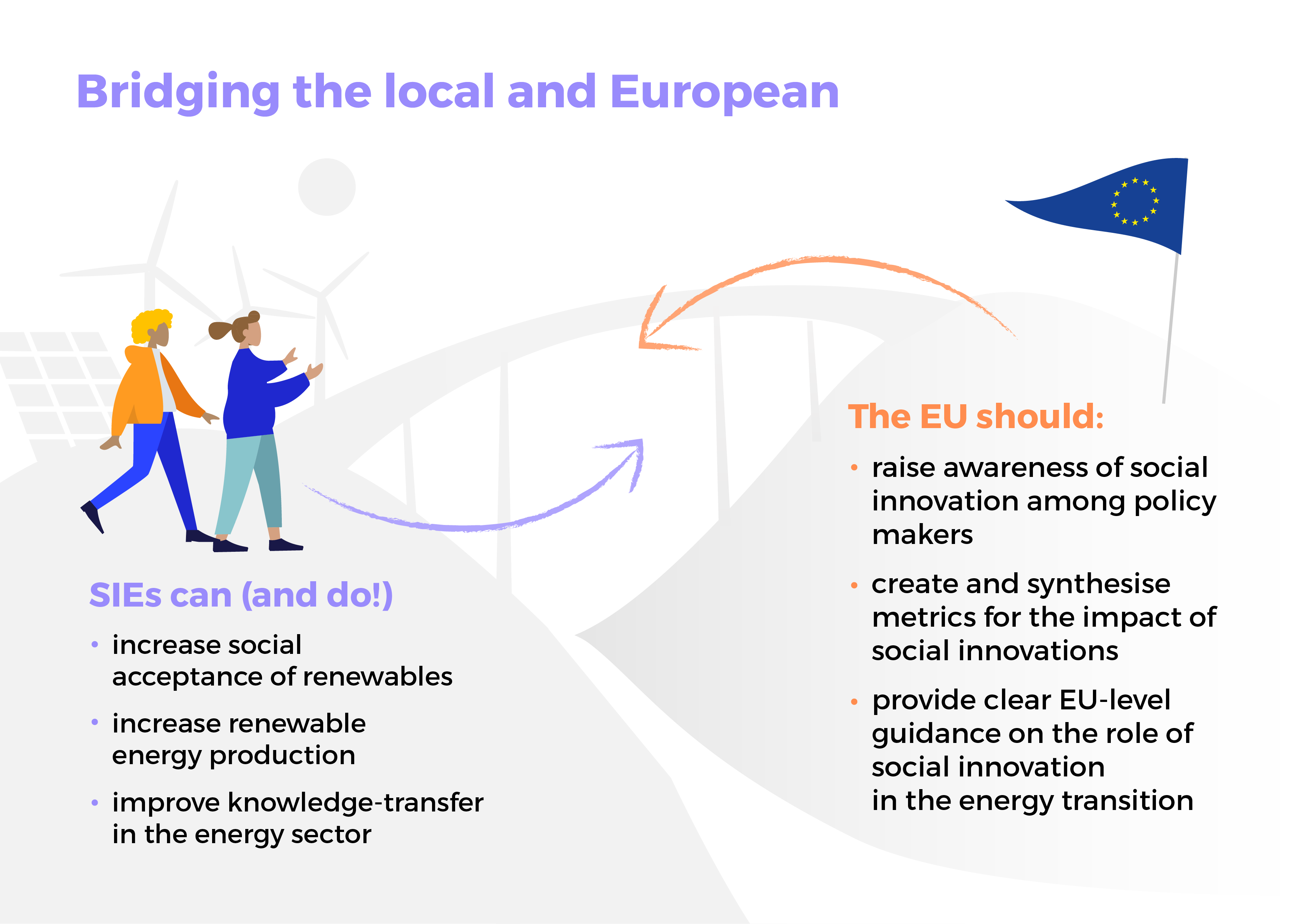
SONNET Infographic #5: Creating a bridge to illuminate how the local and European levels can support each other in achieving energy transitions
April 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. The fifth Energy Read connects SIE work at the local and EU levels. This complimentary infographic distils findings, showing a way to bridge on-the-ground SIE-initiatives and EU policy-makers.
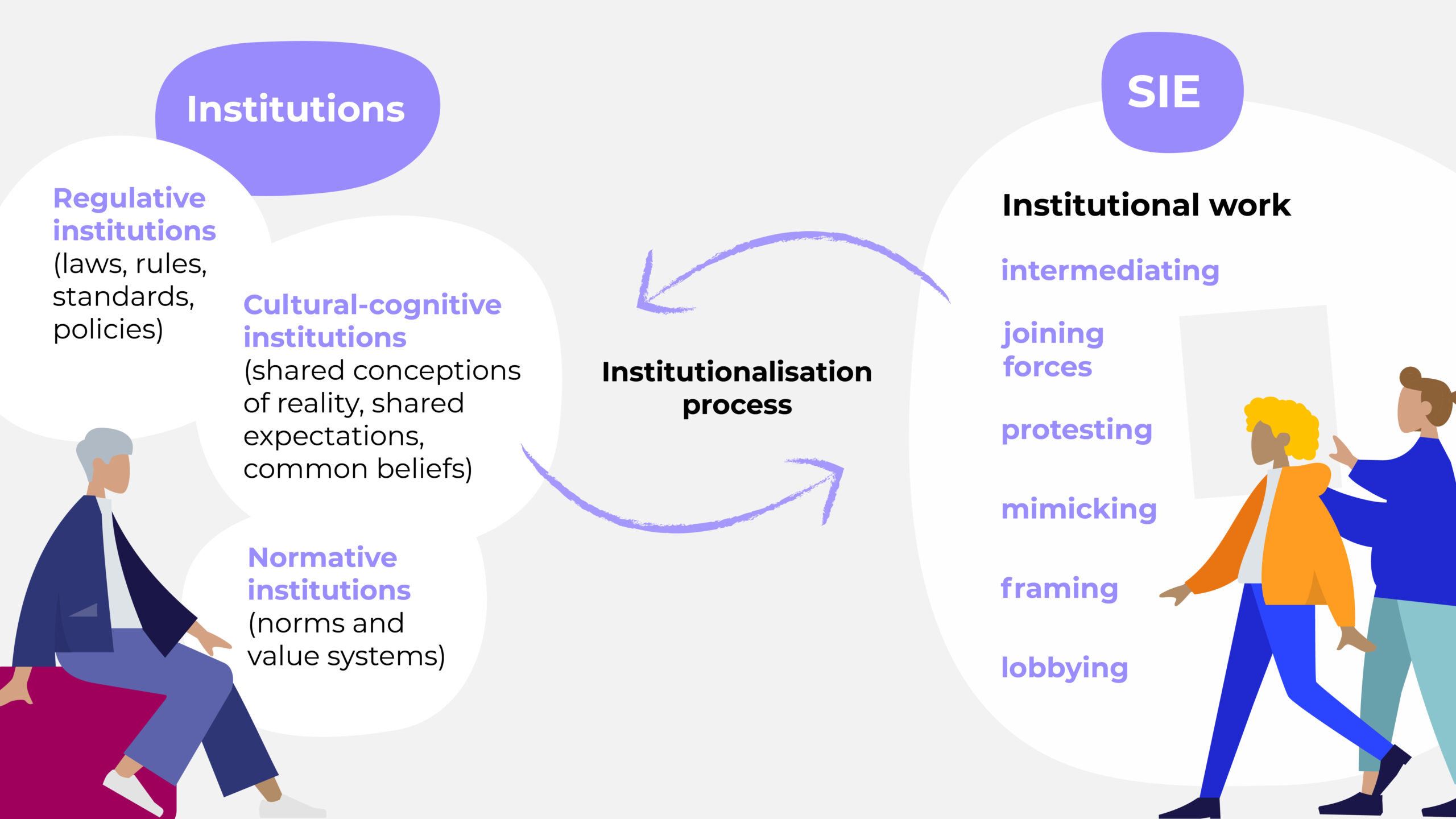
SONNET Infographic #4: An overview of how “institutionalisation” helps understand social innovations in energy (SIE)
April 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. The fourth Energy Read defines and makes use of the concept of “institutions” to overview how social innovations can be (and are!) transformative. This complimentary infographic helps to better understand and define these terms.
SONNET Infographic #3: An overview of the six SONNET City Labs
March 2022 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. The third Energy Read overviews key findings from the project’s City Labs, while this complimentary infographic overviews the innovation actions that each City Lab rolled-out.
SONNET Infographic #2: Compiling Case Studies that explore how social innovations in energy shape – and are shaped by – larger systems
November 2021 – Download
Throughout the project, SONNET is producing a series of so-called ‘Energy Reads’ that summarise the key points from its diverse catalogue of research into concise, accessible, evidence-based publications. The second Energy Read overviews key findings from the project’s 18 Case Studies and three Country Reports, while this complimentary infographic outlines the process of compiling these resources.
SONNET Infographic #1: About the social dimension of energy transitions
June 2020 – Download
In our first SONNET Energy Read, we introduce the concept of social innovation in energy transitions and show their diversity, going ‘beyond only energy cooperatives’. This diversity is portrayed in a typology and illustrated with examples, putting an emphasis on the six cities that are partners in the SONNET project. This complementary infographic brings all of our insights together into one, visual story.
SONNET City Lab Guide
February 2022 – Download
Authors: Agata Dembek, Agata Stasik, Marta Strumińska-Kutra, Alicja Dańkowska
Throughout the SONNET project, we have gathered insights on how to make use of City Labs to drive social innovation in support of sustainable energy transitions. This guide provides background information, a useable checklist, and a series of examples to help local authorities and energy leaders make use of this innovative format to push forward sustainable and just energy transitions.
SONNET Power Guide: unlocking the transformative power of social innovations in energy
November 2021 – Download
Authors: Tessa de Geus, Flor Avelino, Lara Hendrikx, Vaishali Joshi, Naomi Schrandt and Derk Loorbach (DRIFT), Marta Strumińska-Kutra (Kozminski University)
Through research, workshops, and collaborative learning, SONNET has put together a unique and practical guide with evidence-based exercises to help you put power at the centre of your work, in order to unlock the full potential of social innovations to support and push forward energy transitions. With seven ‘building blocks’, seven exercises, and a series of succinct and practical videos, this SONNET Power Guide is an invaluable tool for social innovation practitioners.
SONNET Poster
Authors: Agata Dembek (Kozminski University), Agata Stasik (Kozminski University), Karoline Rogge (University of Sussex)
SONNET aims to co-create a rich understanding of the diversity, processes, contributions, success and future potentials of social innovation in the energy sector (SIE). Our empirical work bridges qualitative and quantitative methodological approaches in an innovative research design. Among other research activities, given its focus on urban areas as major hubs for SIE, SONNET conducts six transdisciplinary SIE City Labs to experiment with new forms of SIE and learn about how multiple actors can harness the potential of SIE
SONNET’s insights regarding cross-cutting issues in sustainable energy transitions
SONNET Deliverable 1.3
May 2022 – Download
Author: Maria Fraaije, Julia Wittmayer, Sabine Hielscher, Marie-Charlotte Guetlein, Christian Winzer, Naomi Schrandt
This working paper aims to synthesise selected insights from SONNET research across the different work streams; specifically, insights on: 1) the factors influencing (enabling or impeding) the development of social innovation in energy, and 2) the contributions that social innovations make to energy systems.
SONNET found several key enabling and impeding factors of social innovation, such as: opposing and locked-in discourses; regulations and beliefs within the regime of the energy sector; contributions of one social innovation enabling others’ success; etc. Furthermore, we found that SIEs contribute to the energy transition in seven ways; this deliverable specifically discusses contributions of social innovation to energy justice and democracy, sustainability, and energy security. The paper closes with recommendations for future research.
The diversity, processes and contributions of social innovation in the energy sector: revised conceptual framework and SIE typology based on SONNET’s empirical evidence
SONNET Deliverable 1.4
May 2022 – Download
Author: Julia Wittmayer, Sabine Hielscher, Naomi Schrandt, Flor Avelino, Karoline Rogge, Marta Struminska-Kutra
This working paper outlines the conceptual advancements developed as part of the SONNET project. First, SONNET developed a typology of social innovation in energy (SIE) and this paper reflects on the usefulness and relevance of this typology. Second, drawing on three bodies of scholarship, SONNET developed six conceptual advancements related to: (1) the understanding of the diversity of social innovation; (2) the multi-actor nature of social innovation; (3) the power dynamics in social innovation and sustainability transitions; (4) the governance of social innovations in cities; (5) broader mobilisation processes as social innovations; and (6) policy mixes for social innovation. Each of these are summarised in this deliverable, including fifteen working propositions which can also practically inform transition processes towards more just, secure, sustainable, competitive, and affordable energy.
Report on scientific conference participation, scientific publications and integration of SONNET results into training programmes
SONNET Deliverable 7.5
May 2022 – Download
Author: Ed Dearnley, University of Sussex (SPRU)
This publication summarises the results of academic dissemination in the SONNET project, split into three distinct areas: scientific publications, presentations (and special sessions) at scientific conferences, and integration of SONNET results into training programmes.
Report on assessment of future potentials of SIE in Europe: business models and competitiveness, future policy interventions
SONNET Deliverable 5.4
March 2022 – Download
Authors: Marie-Charlotte Guetlein, Joachim Schleich
SONNET surveyed 6000 citizens in France, Germany, and Poland, helping us to assess future potential of SIE in Europe. Statistical-econometric analyses investigate factors driving citizen investment in renewable energy projects, participation in renewable energy cooperatives, and purchasing of energy-related mobile phone apps.
Our findings suggest that around 90% of participants in France, Germany and Poland would choose to invest in one of the proposed decentralised renewable electricity generation projects. In addition, 79% of respondents in France would choose to invest in at least one of the energy cooperatives proposed. This suggest high interest in these kinds of projects, and strong future potential for their diffusion.
Report from SONNET on Tour workshops
SONNET Deliverable 7.3
March 2022 – Download
Authors: Adrienne Kotler, Niklas Mischkowski, Olga Krajewska
SONNET hosted two so-called “SONNET on Tour” workshops, to spread its findings to other local authorities and leaders. This publication reports on the outcomes of the workshops, including their agendas and minutes, featuring participants’ reflections and main conclusions. The report has been designed in an easy to read format, including pictures, quotes and other materials that were used in the workshop.
Key outcomes of the workshops were: a set of potential ideas for new City Labs developed by participants in each workshop; a video about social innovation in Bristol showcasing the City Lab themes and approaches; and the establishment of a new and ongoing exchange space for local authorities and SIE initiatives in Poland.
SONNET City Lab Guide
SONNET Deliverable 4.8
February 2022 – Download
Authors: Agata Dembek, Agata Stasik, Marta Strumińska-Kutra, Alicja Dańkowska
Throughout the SONNET project, we have gathered insights on how to make use of City Labs to drive social innovation in support of sustainable energy transitions. This guide provides background information, a useable checklist, and a series of examples to help local authorities and energy leaders make use of this innovative format to push forward sustainable and just energy transitions.
Co-creating strategies for navigating multilevel policy dynamics to encourage SIE – reflections
SONNET Deliverable 2.4
February 2022 – Download
Authors: Karoline S. Rogge, Maria Stadler and Annalena Broich (Fraunhofer ISI), Tessa de Geus (DRIFT), and Sabine Hielscher (University of Sussex)
Contributors: Niklas Mischkowski and Adrienne Kotler (ICLEI Europe), Julia Wittmayer (DRIFT), Agata Stasik (Kozminski University), Adélie Ranville and Anne-Lorène Vernay (Grenoble École de Management), and Daniel Lange (Fraunhofer ISI)
This publication provides guidance on how to better connect with and harness policy dynamics relevant to social innovation in energy at different governance levels. First it lays the foundations needed to explore the opportunities and challenges of better integrating social innovation in the European Fit-for-55 package. Second, it reports on a SONNET policy dialogue that brought local and European leaders together to discussion this integration. Third, it synthesises insights into key reflections, action points, and priority areas.
Report on econometric analysis of SONNET citizen survey, including cross-country comparison on individuals’ perceptions and acceptance of SIE and EU energy transitions
SONNET Deliverable 5.3
December 2021 – Download
Authors: Abigail Alexander-Haw, Elisabeth Dütschke, Valeria Fanghella, Marie-Charlotte Guetlein, Joachim Schleich
This report presents and discusses the statistical-econometric results of the SONNET survey of 6000 respondents in France, Germany and Poland. Results highlight the importance of financial attributes such as the rate of return, the risk associated with such investments, and low minimum investment requirements for investment projects into renewable energy. They also emphasise a role for municipalities matching the investments of citizens. In relation to country differences, we find that citizens in Poland appear more worried about financial risks than citizens in France and Germany. In France, citizens prefer renewable energy cooperatives without the involvement of private companies, a one-member-one-vote rule and cooperatives that allow for high shares of self-consumption. There is generally low interest in gamification in Germany, especially when subscription fees are high. Campaigns in Poland tend to be perceived positively; intentions to act, however, are less pronounced. Campaign arguments stressing the effects of an energy pathway on health and the environment appear more convincing than arguments stressing the effects on innovation and security of supply.
Synthesis report on the comparative analysis of SIE-fields and their SIE-initiatives in six countries: Encouraging the diversity, processes and contributions of SIE
SONNET Deliverable 3.3
November 2021 – Download
Authors: Sabine Hielscher (SPRU), Julia Wittmayer (Drift), Karoline Rogge (ISI), Marfuga Iskandarova (SPRU), Bryony Parrish (SPRU), Anne-Lorene Vernay (GEM), Benedetta Buccolini (Drift)
This deliverable builds on SONNET’s in-depth Case Studies. It dives into comparative analysis of social innovations in energy (SIEs) across focal countries, drawing on specific concepts and empirical phenomena that surface in different cases. It also derives key insights into specific aspects of the diversity, processes and contributions of SIE.
SIE evaluation: Characterising successful SIE to enable secure, sustainable, competitive, and affordable energy transitions
SONNET Deliverable 6.2
November 2021 – Download
Authors: Tim Dzukowski, Leticia Müller, Jonas Schmid, Christian Winzer
Surveys have shed light on how social innovations in energy (SIEs) contribute to reaching EU aims. The first survey demonstrates that SIEs are perceived to contribute towards EU aims related to “renewables production” and lower “CO2-emissions”, which are also the EU aims most important to SIEs. The second survey draws on the SONNET typology, and indicates that SIEs focused on “Organising”-type activities and engaged in the social-relations of “Cooperation”, “Exchange” and “Competition” achieve higher average contribution scores across all aims than SIEs engaged in other types of activities (i.e. “Doing” or “Thinking”) or other types of social relations (i.e. “Conflict”). Follow-up interviews reveal that most SIEs seem not to collect data on their contribution towards meeting EU aims. A workshop identified two promising alternative approaches to quantify contribution: the use of automated media-analysis, and/or data from the database of the European Energy Awards.
Encouraging SIE through strategies for increasing countervailing powers – a practical guide
SONNET Deliverable 2.3
October 2021 – Download
Authors: Tessa de Geus, Flor Avelino, Lara Hendrikx, Vaishali Joshi, Naomi Schrandt and Derk Loorbach (DRIFT), Marta Strumińska-Kutra (Kozminski University)
Contributors: Karoline Rogge and Linda Widdel (Fraunhofer ISI), Magdalena Pitzer and Wouter Mulders (DRIFT), Chris Vrettos (Electra Energy Cooperative), Niklas Mischkowski and Adrienne Kotler (ICLEI Europe), Agata Stasik (Kozminski University), Timo Maas (PBL), Giorgos Koukoufikis (JRC), Marco Costa (AESS)
This practical guide provides readers with evidence-based exercises that they can use to put questions of power at the centre of social innovations in energy, in order to unlock these social innovations’ full potentials to transform systems for the better.
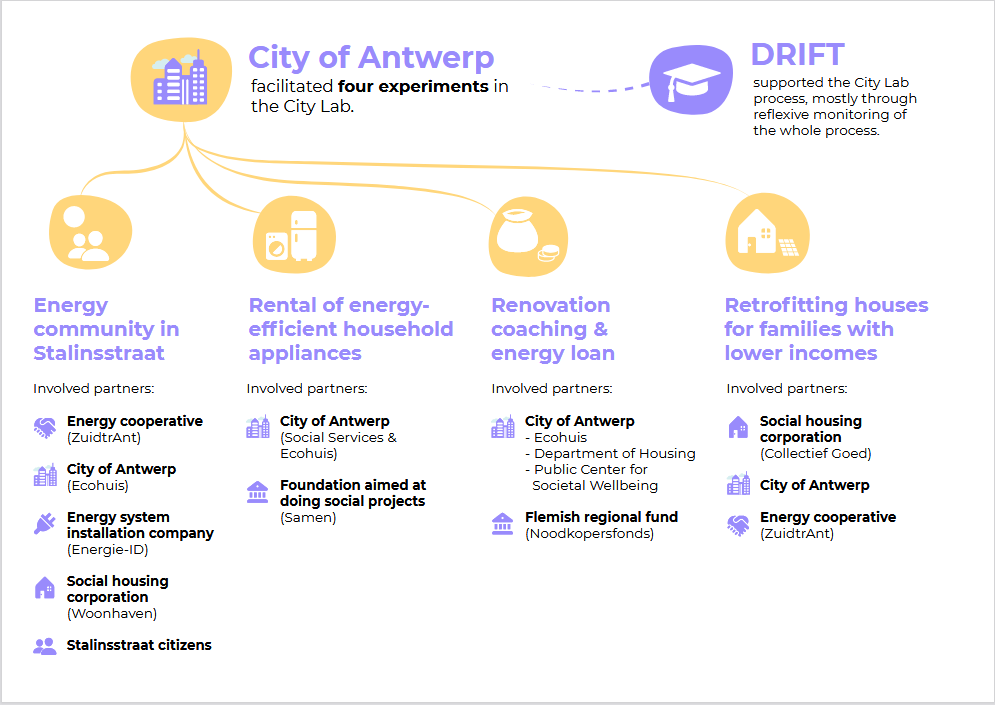
Report on SONNET City Labs
SONNET Deliverables 4.2–4.7
October 2021 – Download: Antwerp, Basel, Bristol, Grenoble, Mannheim, Warsaw
The SONNET City Lab teams – including city and academic partners – produced in-depth reports reflecting on the impacts, successes, and lessons learnt form running City Labs throughout the SONNET project. Each report is city-specific, overviewing: the introduction/context of the City Lab; the City Lab process (including setting the scene, goal-setting, experimentation); and a detailed evaluation of the Lab’s success.
Report on case studies describing the diversity, processes, and contributions of SIEs, SIE-fields and SIE-initiatives in six countries
SONNET Deliverable 3.2
July 2021 – Download
Authors: Sabine Hielscher (SPRU) and Julia Wittmayer (DRIFT)
Contributors: Fabrice Arroyo, Alicja Dańkowska, Agata Dembek, Elisabeth Dütschke, Maria Fraaije, Tessa de Geus, Jasmin Heidary, Marfuga Iskandarova, William Matthews, Julien Lafaille, Wouter Mulders, Leticia Müller, Jörg Musiolik, Adélie Ranville, Sarah Rach, Karoline Rogge, Benjamin Schmid, Naomi Schrandt, Maria Stadler, Agata Stasik, Anne-Lorène Vernay, Devon Wemyss, Linda Widdel
This deliverable presents 18 embedded case studies, which build better understanding of six SIE-fields, which are made up of the social innovation in energy (SIE), actors who work on the SIE (SIE-field-actors), their specific SIE-initiatives, and other field actors who enable or impede the SIE. The case studies are presented in a series of six country reports (three embedded case studies per country report, for 18 case studies total) for France, Germany, the Netherlands/Belgium, Poland, Switzerland, and United Kingdom.
All in all, this deliverable includes an introduction to the case study work (concepts, research questions, methodology), a report structure for the country reports and case studies, and the six country reports in full.
EU and SIE goal alignment map
SONNET Deliverable 6.1
June 2021 – Download
Author: Christian Winzer (ZHAW)
Contributor: Tim Dzukowski (ZHAW)
This deliverable outlines findings based on a survey with SIE representatives, field-actors and researchers, through which SONNET has evaluated to what extent the aims of SIE initiatives are aligned with the goals of EU energy policy. We have found that there is strong alignment with respect to goals to increase renewable energy production and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, while other investigated EU aims were perceived as less important.
Towards a toolkit for harnessing policy networks for encouraging SIE in Europe
SONNET Deliverable 2.2
June 2021 – Download
Authors: Heike Brugger, Iska Brunzema, Maria Stadler (Fraunhofer ISI)
Contributors: Karoline Rogge (ISI); Marta Struminska-Kutra, Agata Dembek, Boleslaw Rok (ALK); Flor Avelino, Sarah Rach, Naomi Schrandt (DRIFT); Regina Betz, Lukas Braunreiter (ZHAW); Marfuga Iskandarova, Sabine Hielscher (UoS); Pascal Bovy, Adélie Ranville (GEM)
This report aims to identify, for each of the six SONNET cities, the policy network in which SIE initiatives are embedded. A policy network analysis is conducted with a particular focus on the relations between key actors at the local, regional, national and EU level (e.g. policy-makers, city administrations, energy utilities, businesses and network organisations), and to identify enabling and impeding structures for SIE initiatives.
Updated Co-creation, Dissemination and Exploitation Strategy
SONNET Deliverable 7.2
January 2021 – Download
Author: Adrienne Kotler (ICLEI Europe)
Contributors: Niklas Mischkowski and Olga Krajewska (ICLEI Europe), Louise Sheridan (University of Sussex), Adélie Ranville (Grenoble École de Management), Christian Winzer (ZHAW School of Management and Law), Karoline Rogge (Fraunhofer ISI)
This deliverable outlines an updated strategy for co-creating knowledge through the SONNET project, as well as for the dissemination and exploitation of SONNET results and learnings. This builds on the original strategy, which was written at the beginning of the project, and it will continue to evolve throughout the second half of the project.
Report on encouraging SIE through collaborative governance arrangements
SONNET Deliverable 2.1
November 2020 – Download
Author: Marta Strumińska-Kutra (Kozminski University)
Contributor: Maria Stadler (Fraunhofer ISI)
This report addresses the questions: ‘What are governance arrangements related to SIE and how (under what conditions) do they evolve over time?’, as well as, ‘How can (novel) governance arrangements encourage the development of SIE?’. To answer these, the publication presents an SIE governance typology, which illustrates the diversity of governance arrangements used by city administrations to facilitate and support SIE, and four propositions to enhance the understanding of SIE governance emergence and institutionalisation. Overall, considering both social interactions (cooperation, exchange, competition, conflict), and governance modes (hierarchical, market-based and network-based), the publication explore what approaches cities can take (and are taking) to steer issues related to social innovation in energy.
Methodological guidelines for case study analysis
SONNET Deliverable 3.1 (April 2020) – Download
Authors: Sabine Hielscher (SPRU), Julia Wittmayer (DRIFT), Rachael Durrant (SPRU)
SONNET aims to co-create a rich understanding of the diversity, processes, contributions, successes and future potentials of social innovation in the energy sector (SIE). This deliverable addresses SONNET’s objective to identify and analyse enabling and impeding factors for SIE processes. It provides a joint research protocol for the case studies.
Report on transdisciplinary research protocol for six co-creating SIE city labs
SONNET Deliverable 4.1 (March 2020) – Download
Authors: Agata Dembek, Alicja Dańkowska, Marta Strumińska-Kutra (Kozminski University)
Report on SONNET’s initial conceptual framework
SONNET Deliverable 1.2 (March 2020) – Download
Authors: Julia M. Wittmayer (DRIFT), Sabine Hielscher (University of Sussex), Karoline S. Rogge (University of Sussex) and Flor Avelino (DRIFT)
While there are many insights on social innovation on the one hand, and energy systems and their social processes on the other – to date these insights have hardly been brought together. In this report, we build on literature that examines processes of social innovation and their institutionalisation and relate it to insights from sustainability transitions and energy research in social sciences to build a draft conceptual framework for the study of diversity, processes and contributions of social innovation in energy (SIE).
Report on preliminary typology of social innovation in the energy sector
SONNET Deliverable 1.1 (January 2020) – Download
Authors: Julia M. Wittmayer (DRIFT), Maria Fraaije (DRIFT), Sabine Hielscher (University of Sussex), and Flor Avelino (DRIFT)
SONNET aims to co-create a rich understanding of the diversity, processes, contributions, successes and future potentials of social innovation in the energy sector (SIE). This report explores the diversity of SIE in Europe and captures it within a comprehensive SIE typology.
Co-creation, Dissemination and Exploitation Strategy
SONNET Deliverable 7.1 (September 2019) – Download
Authors: Adrienne Kotler (ICLEI Europe), Ania Rok (ICLEI Europe), Anja Härtwig (ICLEI Europe), Niklas Mischkowski (ICLEI Europe), Nora Blascsok (University of Sussex) and Olga Krajewska (ICLEI Europe)
The co-creation, dissemination and exploitation strategy of SONNET describes how the knowledge and experience of consortium partners will be used for communicating about the project, disseminating its results to a wide range of audiences and ensuring that the resulting ideas, methods and recommendations are taken up and continued to be used after the project ends (exploitation).
Applying policy mix thinking to social innovation: from experimentation to socio-technical change
Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, Volume 47, 2023
March 2023 – Download
Authors: Karoline S. Rogge, Maria Stadler
So far, the emerging literature on policy mixes for sustainability transitions has paid little attention to social innovation. This seems at odds with recent claims that transformative policies should promote a wide range of innovation, and social innovation in particular. In this paper, we explore whether and how policy mix delineation and analytical approaches that were developed primarily with technological innovation in mind can be usefully applied to social innovation. We examine empirical case study evidence, and proceed in two steps: after an initial top-down mapping of the focal policy mix for social innovation in energy in Germany, we conduct a bottom-up mapping of the policy mix relevant for the social innovation field of ‘participatory incubation and experimentation’ in Germany’s energy sector. Based on our insights we discuss the relevance and recognition of social innovation in sustainability transition policy mixes, and offer research and policy implications for accelerating socio-technical change.
Making sense of power through transdisciplinary sustainability research: insights from a Transformative Power Lab
Sustainability Science, Volume 18, 2023
March 2023 – Download
Authors: Tessa de Geus, Flor Avelino, Marta Strumińska-Kutra, Magdalena Pitzer, Julia M. Wittmayer, Lara Hendrikx, Vaishali Joshi, Naomi Schrandt, Linda Widdel, Maria Fraaije, Marfuga Iskandarova, Sabine Hielscher & Karoline Rogge
If transdisciplinary sustainability research is to contribute to sustainability transitions, issues of power dynamics need to be understood and accounted for. However, examples of concrete methods that put this into practice are sparse. This paper presents a conceptual and methodological framework that develops a better understanding of the power phenomenon, while providing actionable knowledge. By focussing on the context of social innovation in energy transitions, we demonstrate how different theoretical conceptualisations of power can be translated into a collaborative, transdisciplinary research design. In a facilitated process, researchers, policy workers and practitioners from diverse social innovation fields developed and tested the Transformative Power Lab approach and co-wrote a ‘Power Guide’ as a strategic exploration of power dynamics in sustainability transitions, specifically regarding social innovation in energy transitions. Based on the insights that emerged during this process, we discuss how transdisciplinary and action-oriented approaches in sustainability transition studies might benefit from this approach and, potentially, develop it further.
Fit for social innovation? Policy reflections for EU energy and climate policy making
Oxford Open Energy, Volume 2, 2023
January 2023 – Download
Authors: Karoline S Rogge, Maria Stadler, Tessa de Geus, Sabine Hielscher, Julia Wittmayer, Annalena Broich, Adrienne Kotler, Niklas Mischkowski, Agata Stasik, Adélie Ranville, Anne-Lorène Vernay
Achieving climate-neutrality by 2050 and intermediary reduction targets by 2030, requires accelerating the transformation of our systems of production and consumption. While it is widely acknowledged that ambitious climate and energy policies are needed to accelerate such transition processes, research and practise have largely focused on their importance for spurring technological innovation. In this research perspective, we argue that energy and climate policy making should pay more attention to social innovation, as a much-needed additional puzzle piece crucial for successful decarbonisation. Social innovation is diverse, ranging from renewable energy cooperatives, to participatory incubation and experimentation, crowdfunding, local electricity exchange, and more. Based on a literature review that informed a policy dialogue among policy makers, practitioners and researchers, and followed by a workshop with city administrations, twelve practical, co-created action points are outlined on how to better consider social innovation in energy and climate policy making in the EU (and beyond). We thereby hope to stimulate a broader discourse on the dual need for social and technological innovation for reaching climate-neutrality.
Social movements in energy transitions: The politics of fossil fuel energy pathways in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Poland
The Extractive Industries and Society, 2022, 101073
April 2022 – Download
Authors: Sabine Hielscher, Julia M. Wittmayer, Alicja Dańkowska
Pathways towards low-carbon energy transitions have become a priority in 21st century Europe. Commitment to lowering carbon dioxide emissions have triggered changes to current fossil fuel-based energy systems. Over the past decade, fossil fuel energy pathways have been characterised by closures of sites, continued extractions and new explorations, demonstrating processes of (dis)continuation. This paper draws attention to the contentious politics in sustainability transitions and the role of social movements, drawing on case study work that traces social mobilisation alongside key policy and industry developments linked to onshore oil and gas and coal projects in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Poland. Drawing on the notion of scalar practices, we identify political strategies and opportunities for the discontinuation of fossil fuels, and examine how political spaces are impinged and closed down to support continuation processes. Our analysis demonstrates how decision-making powers and possibilities for scrutinising and taking actions against fossil fuels are negotiated between local and central governments, local communities and residents, grassroots movements, national NGOs, and fossil fuel industries. We conclude that all actors are involved in scalar practices, and non-fossil energy pathways remain challenging if the government and industry actors keep trying to displace the politics linked to fossil fuel energy.
Tangled transitions: Exploring the emergence of local electricity exchange in France, Switzerland and Great Britain
Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 180 (2022) 121677
April 2022 – Download
Authors: Marfuga Iskandarova, Anne-Lorène Vernay, Jörg Musiolik, Leticia Müller, Benjamin K. Sovacool
Local electricity exchange is often praised for its ability to empower consumers and benefit communities. In this paper, we investigate and compare the development of local electricity exchange practices in three European countries: France, Switzerland, and Great Britain. We ask: how do local electricity exchange practices and markets vary across national contexts? What are their dynamics of ownership and consolidation, if any? What areas of contestation or disagreement emerge?
To answer these questions, we first briefly define and conceptualise local electricity exchange and its categories, before diving into our research, consisting of document analysis, 40 expert interviews, and observational data from seven meetings and events. Comparing the cases reveals: the complexity and variation of local electricity exchange across the three national contexts; how such acts of decentralisation in turn (and perhaps unpredictably) consolidate power among incumbent actors; and how local electricity exchanges are prone to significant contestation and disagreement. Moreover, comparison reveals competing dynamics of centralisation and shifting forms of ownership.
We conclude by noting: (i) local electricity exchange has as much potential to cement conventional actors and power relations in the sector as it does to support new actors or transform power relations; (ii) approaches to local electricity exchange vary considerably across national contexts and are strongly linked with institutional frameworks and policy regimes; and (iii) the future merits of local electricity exchange are prone to great uncertainty and contestation.
A typology for unpacking the diversity of social innovation in energy transitions
Energy Research & Social Science, Volume 88 (2022) 102513
January 2022 – Download
Authors: Julia M. Wittmayer, Sabine Hielscher, Maria Fraaije, Flor Avelino, Karoline Rogge
While research and policy have, for a long time, focused on energy transitions to address climate change, the concept of ‘social innovation’ has only recently been taken up. Moving beyond narrow perspectives on social innovation, this article asks how we can capture the diversity of social innovation, using the example of the energy sector. It proposes a comprehensive typology of social innovation that captures its empirical diversity, and helps more systematically investigate processes of social innovation and their contributions to making socio-technical systems more sustainable. The typology is based on a conceptual understanding of social innovation in energy (SIE) as comprising changing social relations involving new ways of doing, thinking and/or organising energy. It is empirically grounded in mapping and analysing 500 SIE-initiatives across eight European countries. It opens the possibility to publicly discuss diverse social innovations and their transformative potentials in energy transitions.
Taking power seriously: Towards a power-sensitive approach for transdisciplinary action research
Futures, Volume 135 (2022) 102881
December 2021 – Download
Authors: Marta Strumińska-Kutra, Christian Scholl
This paper focuses on transdisciplinary action research to explore the key challenge of post-normal science – how to deal with power. First, the paper reviews the literature on stakeholder inclusion and identifies a methodological dilemma trapping transdisciplinary action research between the promise of effectiveness and inclusiveness and the danger of power asymmetries affecting the research process and outcomes. We then develop a framework distinguishing three different power-related tensions permeating transdisciplinary research promises: the systemic level of institutions, the heterogeneous stakeholder group, and the role and position of the researcher. We provide concrete literature-based tools for dealing with each of these tensions and mould a power-sensitive approach for transdisciplinary action research.
Who finances renewable energy in Europe? Examining temporality, authority and contestation in solar and wind subsidies in Poland, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom
Energy Strategy Reviews, Volume 38 (2021) 100730
November 2021 – Download
Authors: Marfuga Iskandarova, Agata Dembek, Maria Fraaije, William Matthews, Agata Stasik, Julia M. Wittmayer, Benjamin K. Sovacool
This paper explores the development of financing and subsidies for renewable energy in three fossil-fuelled European countries: Poland, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. Financing for renewable energy is an existing arena involving multi-actor activities and practices that develop and implement (innovative) financial instruments to facilitate investments in renewable energy. The paper focuses on different financial mechanisms – such as grants, awards, subsidies, crowdfunding, community bonds, ventures, social investment – as long as these funding instruments finance sustainable energy infrastructure and activities. The extent to which this is changing social relations and comes with new ways of doing, thinking and/or organizing is an empirical topic explicitly examined in the study.
We first briefly define and conceptualize financial mechanisms and subsidies before explicating our mixed methods research design consisting of scoping, document analysis, 22 original expert interviews, and observational data from eight meetings and events. We then compare the recent history of solar and wind energy financing and subsidies in our three countries. These comparative cases reveal the temporality of subsidization, indicating fundamental changes in the patterns and logics of financing over the past two decades. They reveal shifts in authority and an expansion of actors involved in financing. They lastly reveal tensions and contestations in financing, including gaps in coverage and conflicts among stakeholder groups. We conclude with future insights for renewable energy diffusion, innovation, and policy.
Soziale Innovation als Treiber städtischer Energiewenden: Energiewende, Transformation, soziale Innovationen, Stadtlabore, Bürgerbeteiligung
Transforming Cities magazine, 2|2021
June 2021 – Read the SONNET article – Subscribe to access the magazine
Authors: Viktoria Reith and Sabrina Hoffmann (City of Mannheim), Maria Stadler and Karoline Rogge (Fraunhofer ISI), Niklas Mischkowski and Adrienne Kotler (ICLEI Europe)
Die Veränderung von Städten hin zu nachhaltigen, sozial und ökologisch verträglichen und lebenswerten Räumen erfordert Innovationen in ganz verschiedenen Bereichen. Während Innovationen als Treiber gesellschaftlicher Veränderungen lange Zeit vor allem im Bereich technischer Entwicklungen verortet wurden, wächst inzwischen das Bewusstsein dafür, dass soziale Innovationen als Motor gesellschaftlichen Wandels einen entscheidenden Beitrag zur Gestaltung nachhaltiger und lebenswerter Städte leisten können. Gerade im Energiebereich sind soziale Innovationen jedoch bislang wenig untersucht. Das Fraunhofer-Institut für System- und Innovationsforschung (ISI), ICLEI Europe und die Stadt Mannheim arbeiten gemeinsam an genau diesem Thema: Soziale Innovation in der Energiewende.
Smart grids and institutional change: Emerging contestations between organisations over smart energy transitions
Energy Research & Social Science, Volume 74 (2021) 101974
February 2021 – Download
Authors: Friederike Rohde, Sabine Hielscher
Smart grids are promoted as promising pathways for dealing with new grid challenges that have arisen by the introduction of renewable energies. In Germany, increasing shares of volatile renewables have led to a growing number of smart grid pilot projects and related regulatory and market developments. Even though much has been done to develop the smart grid, significant difficulties remain, in particular, the re-negotiation of new roles and responsibilities of the organisational actors involved. From a sociological perspective, these shifts imply changes to current institutional arrangements within energy systems.
Drawing on new organisational institutionalism and a qualitative analysis of German smart grid developments, this paper sheds light on organisations’ differing practices aimed at creating, maintaining and disrupting institutions (i.e. institutional work). The paper demonstrates how organisations within smart grid developments attempt to reconfigure institutional arrangements in diverging or even contradictory ways. The paper reveals how the re-institutionalisation processes related to smart grids require fundamental changes in the common meaning system. Implementing these changes will remain a challenge if actors try to maintain existing institutional arrangements.
Introduction: Action Research, Policy and Politics. Special Issue of the International Journal of Action Research
Special Issue of the International Journal of Action Research (2021)
January 2021 – Download
Authors: Julia Wittmayer, Koen Bartels, Miren Larrea
This editorial is an introduction to a special issue on the need to connect across different fields to address societal problems, including climate change and social justice.
Consumers or users? The impact of user learning about smart hybrid heat pumps on policy trajectories for heat decarbonisation
Energy Policy, Volume 148 – Part B (2021) 112006
November 2020 – Download
Authors: Bryony Parrish, Sabine Hielscher, Timothy J. Foxona
Decarbonisation policies often emphasise the uptake of new end-use technologies, seeing people as consumers of technologies with predictable impacts. In the UK, smart hybrid heat pumps (SHHP) have attracted policy interest as a technology potentially offering multiple benefits for home heat decarbonisation.
This paper draws on domestication theory, a perspective that frames people as users who actively learn about technologies, to analyse interviews and observations with installers and users involved in the first UK trial of SHHP. This reveals that users’ learning about SHHPs may erode part of the energy savings they offer and have implications for future technology uptake. It also reveals opportunities for policy making to influence user learning, which could be supported by engaging with users as their learning emerges over time. Overall, the paper highlights the policy relevance of technology use, as well as uptake, and adds to calls for energy policy to think beyond information provision and economic incentives to engage with households, implying a less deterministic approach to policy making.
Beyond instrumentalism: Broadening the understanding of social innovation in socio-technical energy systems
Energy Research & Social Science 70 (2020) 101689
July 2020 – Download
Authors: Julia M. Wittmayer (DRIFT), Tessa de Geus (DRIFT), Bonno Pel (DRIFT/Université Libre de Bruxelles), Flor Avelino (DRIFT), Sabine Hielscher (SPRU), Thomas Hoppe (TPM), Susan Mühlemeier (AES), Agata Stasik (Kozminski University), Sem Oxenaar (DRIFT), Karoline S. Rogge (SPRU/Fraunhofer ISI), Vivian Visser (ESSB), Esther Marín-González (CE3C), Merel Ooms (Platform31), Saskia Buitelaar (Platform31), Chris Foulds (Anglia Ruskin University), Kristian Petrick (Eco-Union), Salvador Klarwein (Eco-Union), Seweryn Krupnik (Jagiellonian University), Gerdien de Vries (TPM), Aleksandra Wagner (Jagiellonian University), Anja Härtwig (ICLEI Europe)
Social innovation is an important dimension of current transformations in energy systems. It can refer to alternative business models, novel policy instruments, financing schemes, participatory governance approaches to energy questions, or new discourses. Its significance for energy systems is often considered in narrow instrumentalist terms, reducing it to a tool serving particular policy objectives. Grounding the concept in social science and humanities insights, this review essay proposes a broadened social innovation understanding. We propose 1) to open up the normative complexity of the concept; 2) to appreciate the multi-actor nature of social innovation; 3) to understand it as an analytical entry point for socio-material intertwinement; and, 4) to understand social innovation as premised on experimentalism-based intervention logics. The proposed social innovation understandings provide a broader imagination and strategizing of structural changes in energy systems.













































 The project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 837498.
The project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 837498.